What are the Differences Between Sales Order and Purchase Order?
What Is a Sales Order?
In any B2C or B2B transaction, the sale order is a legally binding document between the seller and buyer. Usually, they are issued after a customer pays, but they can also be issued on credit.
A Sales Order is often issued based on the Purchase Order, and it contains details such as:
- Name and address of the buyer
- Order number for sales
- The billing address if it differs from the shipping address
- Name of the goods or service
- The quantity and price of goods
- Payment terms and conditions
- Estimated delivery date
- Sale terms and discounts (if any)
- The code of goods (if any)
In supply chain management, issuing a sales order is mandatory. A seller is responsible for fulfilling a purchase order submitted by a customer. With large companies, this can become a complicated process. The purpose of sales orders is to provide that orders are fulfilled accurately by obtaining critical information from POs. Also, by making a sale order, a seller makes sure that their inventory is updated on time and correctly.
According to the Sales Order, the accountant sends a tax invoice to the buyer following e the fulfilment of the sale order.
What Is a Purchase Order?
Purchase orders obligate the buyer to acknowledge the delivery of goods in accordance with the specifications. Upon receiving the purchase order, the buyer makes a payment.
It is possible to issue a purchase order digitally or on paper. Digital purchase orders simplify the entire process by tracking purchase orders, processing payments, and reporting. Large businesses negotiate with suppliers, while small businesses use direct purchasing transactions.
The financial terms and other criteria in purchase orders can be more easily negotiated by large companies, reducing the need for frequent bargaining. A company also benefits from this when market conditions fluctuate unexpectedly.
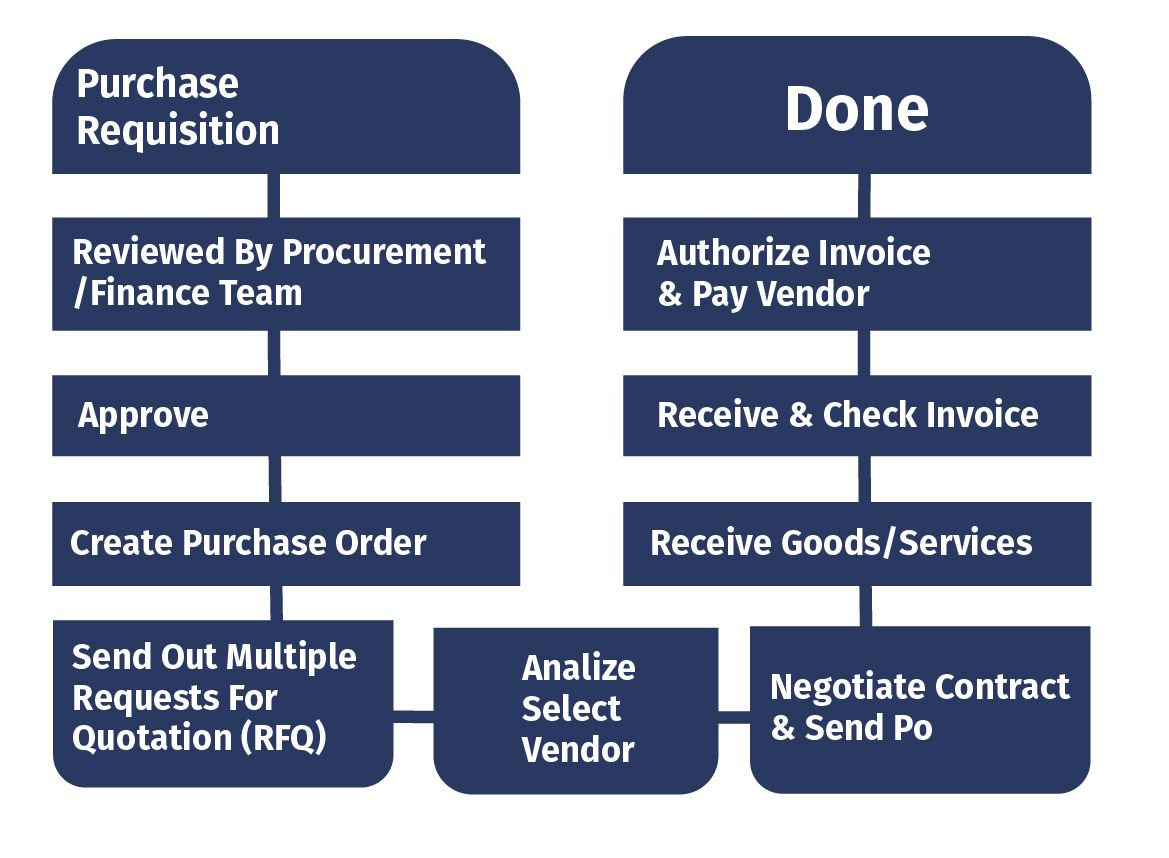
When do we issue a purchase order?
As the last step in the purchasing process, the purchase order acts as a legally-binding document on both sides when the supplier confirms the order.
Here are the details that we need to take into account for issuing a Purchase Order:
- Seller contact details
- Order number
- The name and code of goods
- Purchase goods description
- Price, quantity and the total amount
- Shipping and delivery information
- Payment terms and conditions
- Discounts (if any)
In order for sellers to make financial forecasts and estimates in the long term, purchase orders should always be kept up to date, especially if we place recurring orders with the same supplier.
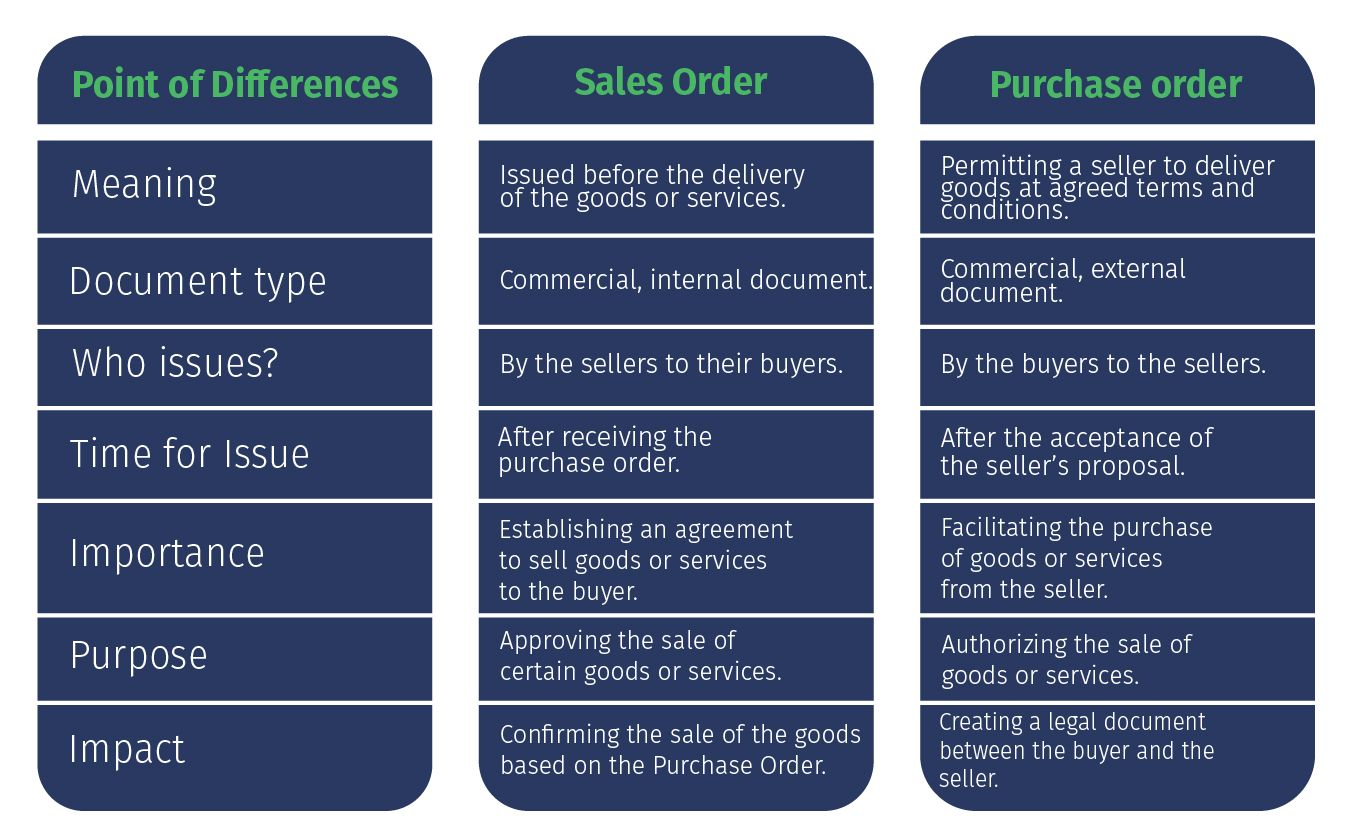
What are the Differences Between Sales Orders and Purchase Orders?
As Sales Orders and Purchase Orders are very closely related, we make the table below to help you better understand the difference between them.
How do Sales and Purchase Orders work together?
- The purchase order is an outline of the purchase from a seller that is created when large companies need to purchase goods.
- The next step is to check the inventory and issue a sales order for items in stock and ready to ship.
- The seller sends the buyer a sales order, which confirms approval of the order. Sales Order contains specifications and payment terms for goods ready for shipping, while stock-out items are listed as backorders with an estimate of when they will be delivered.
- In order to detect any discrepancy, for example, price or quantity differences, the buyer compares the terms of the sales order and the purchase order.
- Separate sales orders will be issued based on the information in Purchase Order for items that will be delivered or will be delivered to multiple locations.
- The buyer receives the goods along with a delivery challan listing the items on the Sales Order.
- The buyer sends a receipt to the seller to inform them that the goods have been delivered.
- The Seller issues a tax invoice to customers along with delivery challan and purchase order.
- The transaction ends when the buyer makes a payment.